Cannabis cultivation in the open air can be a gratifying, cost-effective, and environmentally beneficial activity. Read on to learn how to enjoy homegrown cannabis, especially if this is your first time cultivating.

Selecting a Strain

The strain you grow is determined by your surroundings.
Sativas, in general, are most suited to tropical areas with longer growing seasons. Indicas thrive in climates with short growing seasons and wide temperature swings.
Many hybrids, on the other hand, have been created to thrive in certain environments. As you go through the many strains, choose one that is suitable for the outdoor climate where you live.
You should also think about whether you want to grow an auto-flowering or photoperiod strain. Regardless of the light cycle, auto-flowering strains flower within a few weeks after germination. When the days get shorter than the nights, photoperiod strains blossom.
Season of Cannabis Production
From seed to harvest, most cannabis plants will take between 70 and 150 days. Knowing that range and the length of the vegetative stage of the strain can help you figure out when to start growing outside.
During the vegetative stage, cannabis requires a lot of sunlight. When the light cycle gives more uninterrupted darkness than light, they enter the blossoming phase. After the summer solstice, something begins to happen.
During the vegetative stage, cannabis requires a lot of sunlight. When the light cycle gives more uninterrupted darkness than light, they enter the blossoming phase. After the summer solstice, something begins to happen.

Seeds vs Clones

From seed to harvest, most cannabis plants will take between 70 and 150 days. Knowing that range and the length of the vegetative stage of the strain can help you figure out when to start growing outside.
During the vegetative stage, cannabis requires a lot of sunlight. When the light cycle gives more uninterrupted darkness than light, they enter the blossoming phase. After the summer solstice, something begins to happen.
Outdoor Climate That Is Perfect
The optimal temperature for cannabis plant growth is around 70 degrees Fahrenheit. Temperatures above 85 degrees F will slow the growth of cannabis plants, while temperatures below 55 degrees F will destroy them.
Cannabis plants prefer humidity levels of 50-55 percent. More than that can result in the growth of mold. A lack of humidity can cause plants to dry up faster than they can replenish from their roots.

Inground vs. Containers

The quality of your inground soil will determine whether you plant in the ground or in a container. Planting weed in-ground provides your plants lots of room to flourish if you have good soil. It also exposes them to healthy microbial life as well as worms, the best soil buddies of all.
Planting cannabis in a container, on the other hand, is a terrific technique to cultivate cannabis outdoors if your soil quality is poor or you have little outdoor space. Grow bags are cloth-covered containers. These containers drain well, don’t get too hot, and endure a long time compared to plastic pots.
The Best Weed-Resistant Soil
Cannabis, like most plants, prefers fertile, well-draining soil. Water is used by cannabis roots to absorb nutrients through their root system. Those nutrients are employed to aid in the growth of the plant. Plants will have a tough time getting the nutrients they require if the soil can’t hold on to water. Too much water in the soil can suffocate the roots and cause root rot.
The growing media you choose should be crumbly, with a nice mix of silt, sand, and organic matter such as wood chips and compost. Peat moss, coco coir, vermiculite, and perlite are examples of aerating materials.

The Seedling Phase and Germination
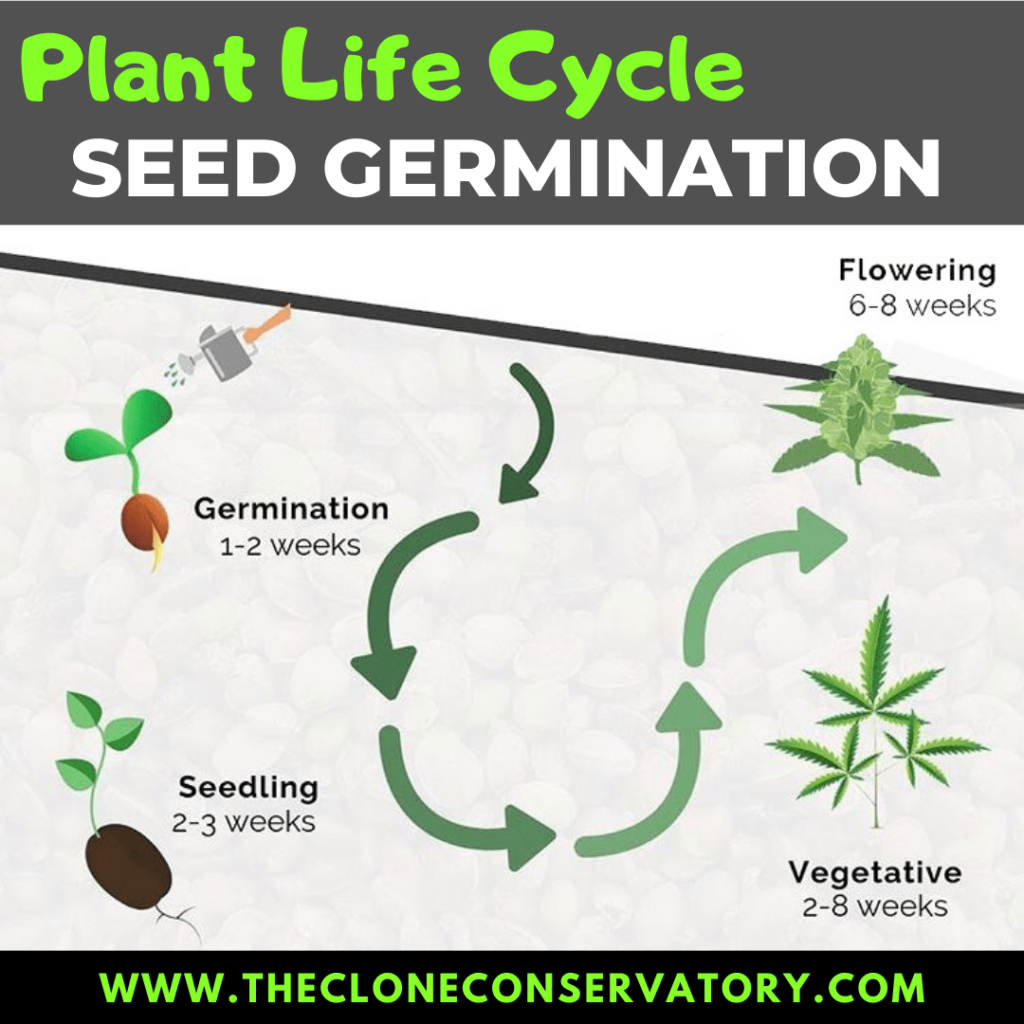
You might be able to start your seeds immediately outside if you reside in a warmer environment. Seedlings, on the other hand, lack the strength to withstand strong winds, temperature changes, and illnesses. Seeds can be started indoors to avoid exposure to these elements.
Cannabis Seedlings Should Be Transplanted Outside
When nighttime temperatures consistently reach 55 degrees F, you can transfer your seedlings outside to an area that receives at least 8 hours of direct light and 18 hours of total light. By the time you’re ready to transplant your seedlings, they should be nearing the end of the seedling phase (approximately 2-3 weeks after germination).

Watering and Fertilizing Your Plant

To develop and blossom, cannabis requires nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) as well as micronutrients. During the vegetative phase, nitrogen is very crucial, whereas potassium and phosphorus are essential for flowering.
Pruning Cannabis Plants
Pruning leaves that touch or are near to touching the soil is a good idea. Diseases can spread throughout the plant if these leaves become infected.




